



 |
 |
Main Menu |  |
 |
|||
| Contacts | FAQ | Links | |||||
 |
||||
| Arctic Seas | NORTH ATLANTIC | South Atlantic | ||
| North Sea | White Sea | BALTIC SEA | Black Sea | Azov Sea |
 |
List of species of Decapoda | |||
| Photo of Decapoda | Habitat | |||
 |
 |
|||
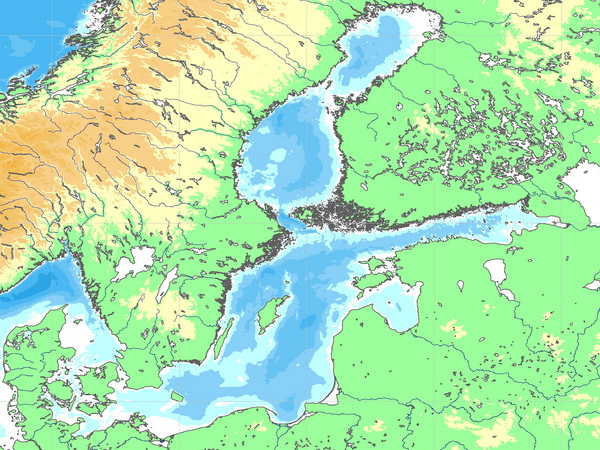
| The Baltic Sea is an inland sea, located in North of Europe. Surface is 419 thousand km². The average depth is 71 m. The salinity of the surface water decreases with distance from the straits - from 11 ‰ to 6-8 ‰ in the central part of the sea. In the Gulf of Bothnia, it is 4-5 ‰, in the Gulf of Finland 3-6 ‰ (at the top of the bay 2 and less). In the deep and bottom layers of water, salinity varies from 16 ‰ in the west to 12-13 ‰ in the central part and up to 10 ‰ in the north of the sea. In the years when the inflow of water increases, salinity in the west rises to 20 ‰, in the central part of the sea to 14-15 ‰, and in the years of decreasing inflow in the middle part of the sea it drops to 11 ‰. | ||||
| A feature of the hydrology of the Baltic Sea is a large excess of fresh water, formed due to precipitation and river runoff. The brackish surface waters of the Baltic Sea drain into the North Sea through the Danish straits, and the deep current into the Baltic Sea is fed with the salty waters of the North Sea. During storms, when the water in the straits is mixed to the very bottom, the water exchange between the seas changes - along the entire cross-section of the straits, water can go to both the North and the Baltic Sea. The tides in the Baltic Sea are semi-diurnal and diurnal, but their value does not exceed 20 centimeters. | ||||
 |
||||
| Full or partial publication of any materials of this site on the Internet is possible only upon receipt of written permission from the site administration with the obligatory indication of direct indexed references to the original material. Full or partial publication of any materials of this site in any other media is possible only by special agreement with the administration of the site www.decapoda.aquarius-s.ru |
||||
 |
|
